
by Editor | Jul 28, 2019 | News
David Bray, one of top 24 Americans under 40 changing the world and also a member of AI World Society Standards and Practice Committee, will visit Vietnam and talk at the Vietnam CEO Summit on August 8, 2019.
He will speak about “Why CEOs Should Embrace Exponential Change, Collaborate, and Co-Existence“. The Vietnam CEO Summit is the conference of CEOs of the top 500 companies in Vietnam, organized by Vietnam Report.
David Bray will also meet and discuss with ICT leaders of Vietnam.
Last year, Professor Jason Furman, who served eight years as a top economic adviser to President Obama, including as the 28th Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers from August 2013 to January 2017, acting as both his chief economist and a member of the cabinet, was the keynote speaker of the conference.
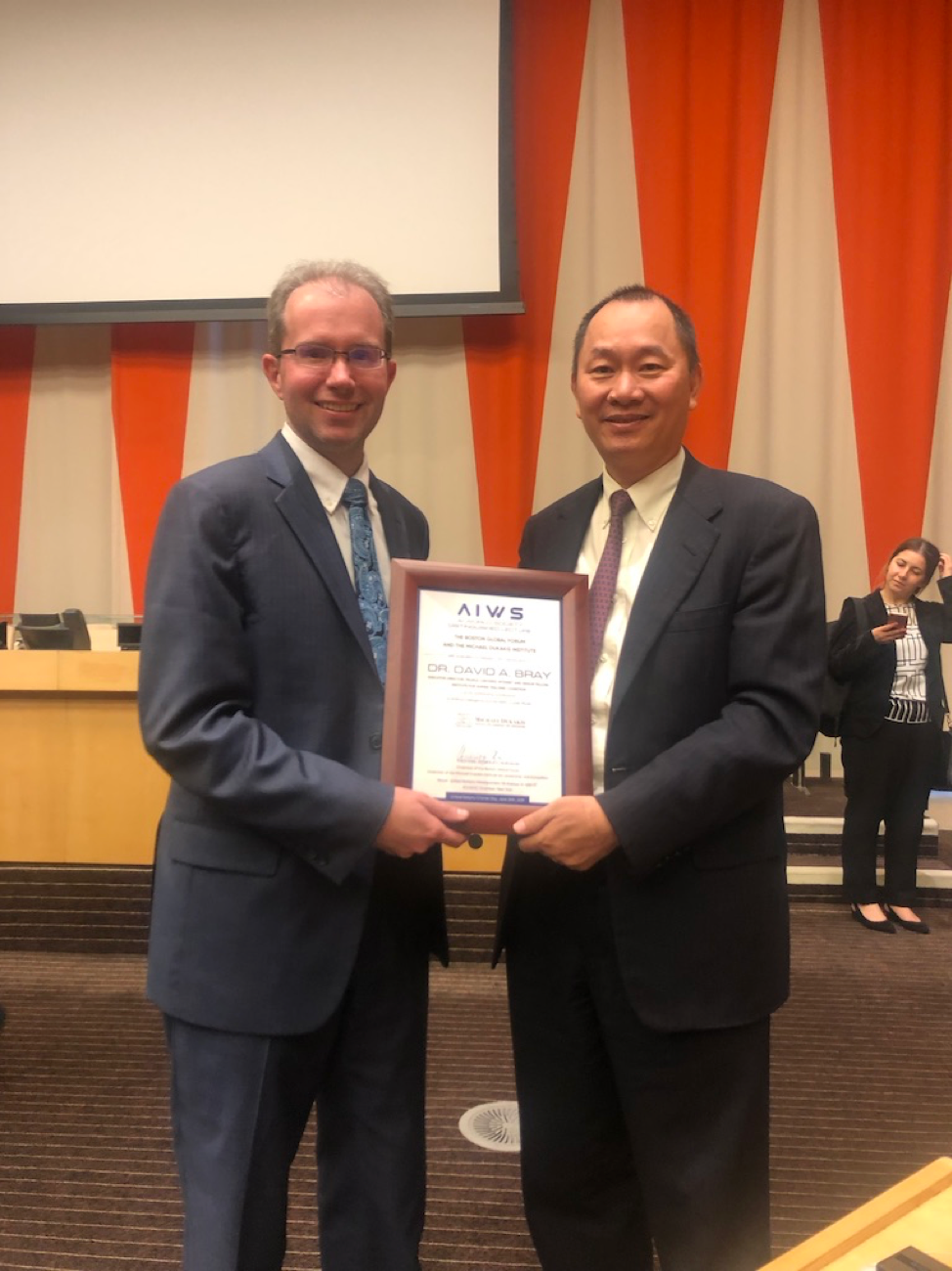
David Bray was the AI World Society Distinguished Lecturer on United Charter Day June 26, 2019 at Headquarter of United Nations.

by Editor | Jul 28, 2019 | News
Microsoft today announced that it would invest $1 billion in OpenAI, the San Francisco-based AI research firm cofounded by CTO Greg Brockman, chief scientist Ilya Sutskever, Elon Musk, and others, with backing from luminaries like LinkedIn cofounder Reid Hoffman and former Y Combinator president Sam Altman. In a blog post, Brockman said the investment will support the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) — AI with the capacity to learn any intellectual task that a human can — with “widely distributed” economic benefits.
To this end, OpenAI intends to partner with Microsoft to jointly develop new AI technologies for the Microsoft Azure cloud platform and will enter into an exclusivity agreement with Microsoft to “further extend” large-scale AI capabilities that “deliver on the promise of AGI.” Additionally, OpenAI will license some of its technologies to Microsoft, which will commercialize them and sell them to as-yet-unnamed partners, and OpenAI will train and run AI models on Azure as it works to develop new supercomputing hardware while “adhering to principles on ethics and trust.” The philosophy on AI Ethics is also initiated by Michael Dukakis Institute for Leadership and Innovation (MDI), which established Artificial Intelligence World Society (AIWS) for the purpose of promoting ethical norms and practices in the development and use of AI.
The original article can be found here

by Editor | Jul 28, 2019 | News
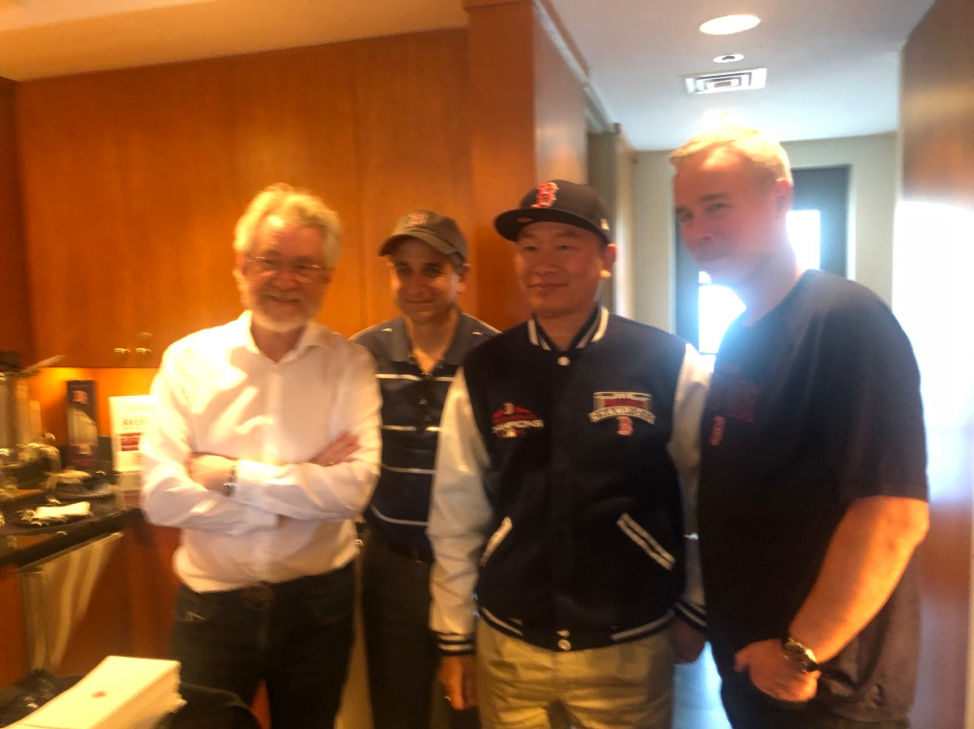
Professor Alex Sandy Pentland, MIT, and Jeff Saviano, Chief of Advanced Global Tax Project of EY, together with the Boston Global Forum and experts of the World Bank and the New American, discussed about applied AI, Blockchain, and Big Data to build the Advanced Global Tax System, as a important part of the AI-Government. They discussed about:
- Influencing taxpayers’ behavior should be an area of focus to develop AI (machine learning) enabled solutions
- How technology (AI in particular) can be leveraged to prompt new and desired behaviors in taxpayers through more effective communications
- How technology-enabled solutions should touch on all the following aspects: (i) enforcement, (ii) compliance, and (iii) trust
The advanced global tax system will be a part of the Social Contract 2020, a project developed by Governor Michael Dukakis, Vint Cerf, one of fathers of Internet, Nguyen Anh Tuan, Professor Alex Sandy Pentland, Professor Nazli Choucri (MIT), Professor Thomas Patterson, and Professor David Silbersweig (Harvard).

by Editor | Jul 21, 2019 | News
The Boston Global Forum honored Professor Joseph Nye as a Distinguished Global Educator for Peace and Innovation on World Reconciliation Day September 9, 2017, at Loeb House Harvard University. He wrote an article in Project-Syndicate about cybersecurity:
“Understanding deterrence in cyberspace is often difficult, because our minds remain captured by an image of deterrence shaped by the Cold War: a threat of massive retaliation to a nuclear attack by nuclear means. A better analogy is crime: governments can only imperfectly prevent it.”.
The post can be found here
by Editor | Jul 21, 2019 | News
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes an increasing part of our daily lives, it’s no wonder that educational institutions are racing to catch up with the need to develop more talent to keep the engine of AI development running. Increasingly, educational institutions from elementary to higher education as well as adult and professional learning are being transformed by intelligent systems that are helping humans learn better and achieve their learning objectives.
AI systems are being used to tailor and personalize learning for each individual student. Through the power of machine learning based hyperpersonalization, AI systems are being used to develop a custom learning profile of each student and customize the training materials for each student based on their ability, preferred mode of learning, and experience. In addition to customized materials, AI systems are being used to augment tutoring with personal, conversational education assistants. These autonomous conversational agents can answer questions from students, provide assistance with learning or assignment tasks, and reinforce concepts with additional materials that can help reinforce the curriculum.
Regarding to AI applications in Education, Michael Dukakis Institute (MDI) is also working with universities and think tanks to share the commitment to the constructive and development of AI for avoiding bias and obtaining core ethical values in the school system and society in general.
The original article can be found here.

by Editor | Jul 21, 2019 | News
WeChat is a window into the future of the internet in many different ways. Based in China and boasting over 1.1 billion global users, it’s one of the world’s most advanced and popular apps.
New research from the University of Toronto’s CitizenLab pulls the curtain back on how WeChat’s real-time, automatic censorship of text and images is used to exert control over political discussion on topics ranging from international issues like the trade war with the US to domestic scandals like the disappearance of court documents in a 2018 dispute between two multibillion-dollar Chinese mining companies. All discussion is ultimately subject to the Chinese government’s approval.
Researchers found that newsworthy events like the arrest of a Huawei executive on charges of fraud and the CRISPR-baby scandal in which a Chinese scientist announced the birth of girls with edited genomes triggered waves of censorship. So did a host of other issues, like conflict with the US and domestic corruption or other problems. According to Michael Dukakis Institute (MDI) and AI World Society (AIWS), AI and advanced technology should be applied and developed to promote ethical norms and practices for helping people achieve well-being and happiness, and it could not be used as a real-time automated censorship for digital dictatorship.
The original article can be found here

by Editor | Jul 21, 2019 | News
Michael Dukakis Institute for Leadership and Innovation announces the AI World Society (AIWS) Young Leader Program. People under 35 years old in the world can apply and attend projects of AI World Society Initiative as build AIWS Ethics Index, the Social Contract 2020, they also can practice leadership by encouraging communities to contribute, practice initiative of AI World Society to build a better world with deeply applied AI and AI for good.
AIWS Young Leaders will be mentored and assisted by leaders and thought leaders in the world such as Governor Michael Dukakis, President Vaira Vike-Freiberga, professor Thomas Patterson (Harvard), professor David Silbersweig (Harvard), professor Alex Sandy Pentland (MIT), professor Nazli Choucri (MIT), Nguyen Anh Tuan, Kazuo Yano, and more.
Michael Dukakis Institute encourage students of universities, high schools in the world to apply and contribute. AIWS Young Leaders can contribute or attend events from their places through online, they do not need to come to Boston. To apply, please send a letter introduce about yourself and your commitment for AIWS Young Leaders Program to [email protected] from August 1, 2019.

by Editor | Jul 21, 2019 | News
In a discussion to build the Social Contract 2020, Professor David Silbersweig, Academic Dean, Harvard Medical School, contributed ideas toward it.
In Internet, Data, and AI age, citizens and governments are connected with TCP/IP Standard of Internet, the Internet dramatically changed the world, and big data and AI continue transform the world with no boundaries and no physical distance. However, there are still differences in political and societal models around the world. Dangerous conflicts still continue this situation in politics.
For a better world, we need a new democracy and new politics as new societal standards to meet requirements of Internet, big data, and AI age. Every countries need to meet with these new society standards to connect each other. If a nation does not meet these standards, they must to be isolated from the rest of the world.

by Editor | Jul 14, 2019 | News
Vint Cerf, one of the fathers of Internet, discuss about The Social Contract 2020:
Vint Cerf recollects the founding of the idea of the social contract by Rousseau, which is about “what the relationship between citizens and the government is.” The people in theory gave up some autonomy in return for safety and a society, which they live in. It makes sense because if that people have the ability to do whatever they wanted, they can do that and no one is safe, but the other end, little freedom of action and limited opportunity was not a good society either.
He was convinced that the introduction of computer-related things, such as computers, the internet, social media, and AI, created a challenge for both governments and citizens. Citizens need to learn to become more literate, eg. knowing which sources are reliable, or deciding informations from search engines are reliable or not. He also note that cultures may react differently to technological developments.
He states that the solutions to these problems would not lie on algorithms, and that these problems actually stems from our cultural and societal norms. It should be solved by ourselves, via debate and discussion. However, it can only be done when there’s a universal underlying technological understanding, and when bad-faith actors are not of concern.
Issues will not go away when lawmakers and people in power “suppress the deficits”, giving examples such as passing a law and not doing anything after that, or writing an algorithm and leaving it as it is. It can only be done when worked with the culture, and helping people understand how technology can be abused and how they can defend themselves.
Boston Global Forum will introduce ideas and discussions of The Social Contract 2020 in future AIWS Summit segments.








