
by Editor | Aug 25, 2019 | News
After news emerged that a multi-disciplinary team led by the University of Surrey successfully filed the first ever patent applications for inventions autonomously created by AI without a human inventor, Ian Bolland caught up with team leader Professor Ryan Abbott about the potential knock-on effect for life sciences.
Professor Abbott began by explaining the potential effects the filing will have on life sciences and other industries.
“These filings are important to any area of research and development as well as any area that relies on patents. Patents are more important in the life sciences than in many other areas, particularly for drug discovery. AI has also been used extensively in the drug discovery process for a long time for tasks like screening of compounds and in silico analysis. These tasks can be the foundation for patent filings.
“As AI is becoming increasingly sophisticated, it is likely to play an increasing role in R&D including in the life sciences. It is an exciting prospect that AI may be able to improve the efficiency of some historically very inefficient practices. Pharma and tech companies are likely to develop AI to automate more and more of the drug discovery process.”
Abbott believes that AI is going to become more autonomous because of its current trends, and its continuing and progressive involvement in R&D. According to Michael Dukakis Institute for Leadership and Innovation (MDI), AI can be an important tool to relieve people of resource constraints and arbitrary/inflexible rules in R&D, but AI algorithms should follow ethical principles that promote fairness and avoid unjust effects on people.
The original article can be found here.
by Editor | Aug 25, 2019 | News
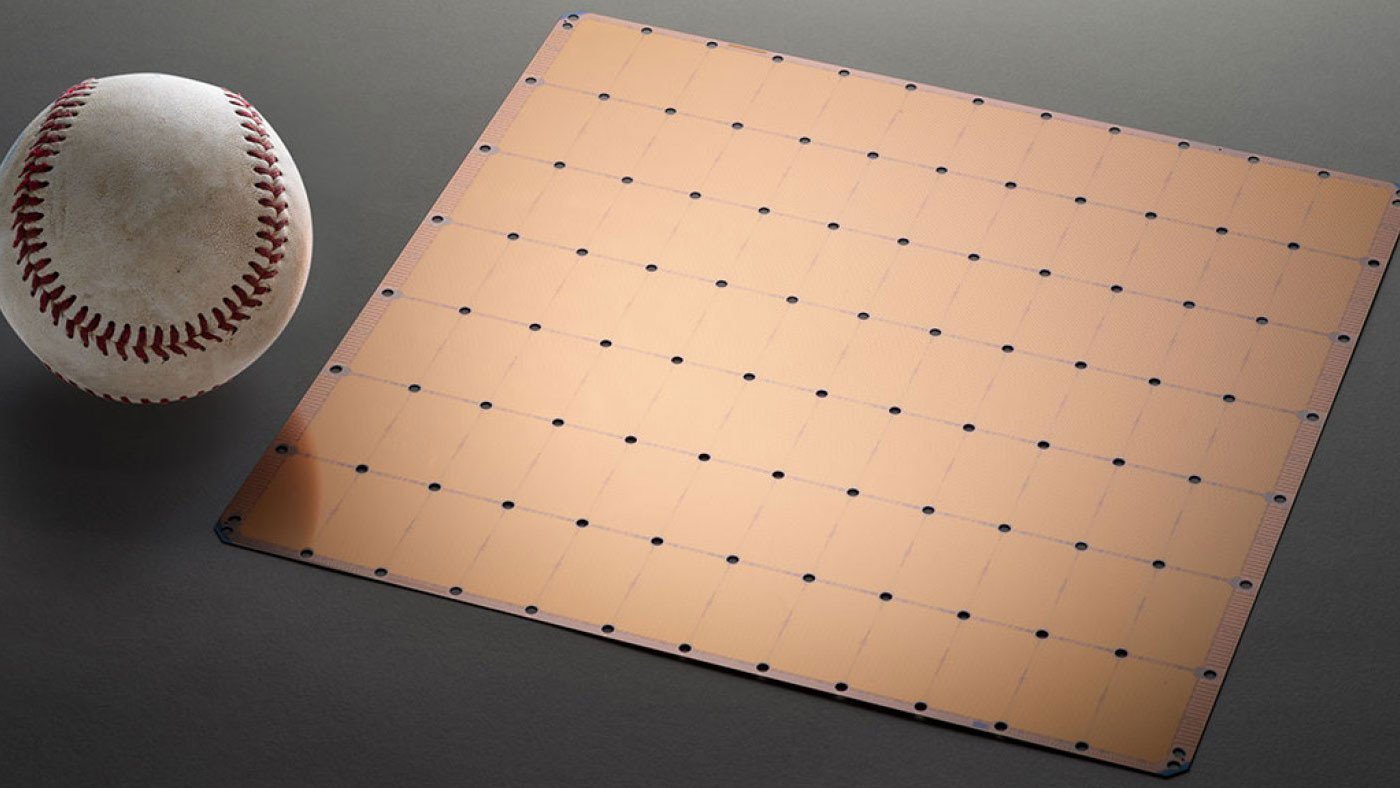
At the Hot Chips conference in Silicon Valley this week, Cerebras is unveiling the Cerebras Wafer Scale Engine. The chip is almost 57 times bigger than Nvidia’s largest general processing unit, or GPU, and boasts 3,000 times the on-chip memory. GPUs are silicon workhorses that power many of today’s AI applications, crunching the data needed to train AI models.
According to Cerebras, is that hooking lots of small chips together creates latencies that slow down training of AI models—a huge industry bottleneck. The company’s chip boasts 400,000 cores, or parts that handle processing, tightly linked to one another to speed up data-crunching. It can also shift data between processing and memory incredibly fast.
If this monster chip is going to conquer the AI world, it will have to show it can overcome some big hurdles. One of these is in manufacturing. If impurities sneak into a wafer being used to make lots of tiny chips, some of these may not be affected; but if there’s only one mega-chip on a wafer, the entire thing may have to be tossed. Cerebras claims it’s found innovative ways to ensure that impurities won’t jeopardize an entire chip, but we don’t yet know if these will work in mass production.
Another challenge is energy efficiency. AI chips are notoriously power hungry, which has both economic and environmental implications. Shifting data between lots of tiny AI chips is a huge power suck, so Cerebras should have an advantage here. If it can help crack this energy challenge, then the startup’s chip could prove that for AI, big silicon really is beautiful.
The original article can be found here.

by Editor | Aug 25, 2019 | News
Professor Alex Sandy Pentland, Director of Connection Science, MIT, and Member of Boston Global Forum’s Board of Thinkers, will speak about the Social Contract 2020 at the World Leadership Alliance-Club de Madrid Conference on October 21, 2019 in Madrid, Spain. He said:
“Social Contract 2020: Data has joined labor and capital as the raw material of prosperity, and so data must also become an integral part of the social contract; to this end I propose a strategy for incorporating both data ownership rights and data governance into our civic systems.”
At the conference, one of topics is “Data Economies and the Future of the Social Contract”. The World Leadership Alliance–Club de Madrid, the largest forum of democratic former Head of States, expects to bring two to three initiatives for concrete action to be taken forward as projects. The Social Contract 2020 will be one of three initiatives of the conference.
The Policy Dialogue on AI and democracy seeks to move the conversation on AI beyond tech and into the democratic governance arena. By bringing together experienced politicians, tech companies, academic researchers, and civil society representatives, it seeks to promote ‘multi-stakeholderism’ in the articulation of informed policy proposals that can effectively turn the design, development and deployment of AI into a driver for democratic innovation and renewal at a time when wide-spread dissatisfaction with the present system and uncertainty about the future are seriously affecting public trust.

by Editor | Aug 25, 2019 | News
Governor Michael Dukakis, co-founder and chairman of the Boston Global Forum, co-founder of the Social Contract 2020, will moderate the AI World Society Conference, with the theme “A Proposed Social Contract 2020, Regarding Rules and International Laws for AI and Internet.”
Professor Alex ‘Sandy’ Pentland, who directs the MIT Connection Science and Human Dynamics labs, co-founder of the Social Contract 2020, noted as one of the “7 most powerful data scientists in the world” alongside the founders of Google and the Chief Technical Officer of the United States, will be the keynote speaker. He will present the concepts of the Social Contract 2020. Dr. Paul Nemitz, Principal Adviser, Directorate General for Justice and Consumers, the European Commission, a member of AI World Society Standards and Practice Committee, will present the Rules and International Laws of AI World Society. Professor Christo Wilson, Harvard Law School Fellow, and Michael Dukakis Leadership Fellow, will present Solutions for AI Transparency.
Other leading global thinkers and leaders will join and discuss at the conference, which will be take place at Harvard University Faculty Club on September 23, 2019.
The extent to which governments and corporations succeed in amassing and using relevant data –the means of production of AI– is set to alter the global economy and the balance of power between states, markets and civil society. The rise of AI is reshaping the geopolitical and societal orders in ways researchers are only beginning to examine.
The use of AI may pose a challenge to democracy, but, if handled correctly, it can also bring more and better democracy. Democratic governments simply cannot afford to lag behind; they must govern the digital game before it governs us all. “The digital is political” and therefore requires a political response: How can we anticipate the fast-changing world of AI and reap the benefits while countering the risks it poses to democracies?
Discussions and matters from this conference will be introduced at the World Leadership Alliance-Club de Madrid Conference in Madrid, October 2019.

by Editor | Aug 11, 2019 | News
Speaking at the Vietnam CEO Summit 2019, titled “Leading Strategy in Digital Transformation and Opportunities for Vietnamese Businesses”, Mr. Jeffrey Saviano, EY Global Tax Innovation Leader and MIT Connection Science Fellow said that Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Blockchain are very important to build a global tax system.
Value-added from Blockchain-based business operation will increase to about USD 176 billion by 2025 and will then skyrocket to USD 3.1 trillion by 2030. However, only 4% of CIOs are actively using AI within their own organization currently. Meanwhile 42% of CIOs are deploying AI development projects.
Mr. Saviano also quoted the report from McKinsey & Company and Gartner, which state that the technology giant such as Baidu and Google have paid USD 20 billion to 30 billion for AI in 2016. By 2021, 40% of new business applications will be equipped with AI technologies. From now to 2030, AI will generate 13 trillion USD of GDP growth (equivalent to 1.2% per year).
US-based companies have made 66% of all investments in AI in 2016. China ranks second with 17%, but is growing very fast. Global business value derived from AI is expected to reach USD 1.2 trillion in 2018 and USD 3.9 trillion in 2022. Cash flow can be reduced by 20% compared to the current if AI technologies are not applied.
Also according to Mr. Saviano, in this year, they built a model of Global Tax System, a kernel of the AI-Government. This will be a pioneering initiative in applying advanced technologies to the most pressing tax issues in the world. Tax digitization trend and shifting focus from tax returns to tax payment by data will become clear. This tax digitization procedure model will extract data directly from source systems and send such data directly to the government. Moreover, the cycle time of this model can be shortened from 3 years to 90 days.
With AI and Blockchain applications, businesses will be able not to declare tax as the usual process. Instead, businesses will take their own data to calculate tax with assistance of AI and then submit directly to the government; the tax authorities only consider whether the enterprise paying such taxes is appropriate. When tax administration will be digitalized at a deeper level, the government must also make it possible to facilitate their own institutions.
Advanced technology capabilities for tax in the coming time will include Document Intelligence (DI), Structured Machine Learning (ML), and Blockchain for supply chain. With AI solutions, time on task has been reduced by 50-70%, accuracy is greatly improved, tax professionals’ satisfaction is much higher and key tax data can be extracted in hours rather than days.
Tax policies and tax management are important to every government. Tax solutions with advanced technologies and the explosion of Blockchain technology with specific applications into business operations have attracted the attention of businesses at the CEO Summit. Most businesses are wondering about which scope to apply Blockchain, how to create value, where to start, and how to do it.
Together with interested parties, such as the World Bank, Boston Global Forum & Michael Dukakis Institute for Leadership and Innovation and MIT Connection Science develop cutting-edge advanced technology based solutions for the benefit of government tax authorities (focused on AI and Blockchain) that will also greatly benefit the private sector. It will open a potential application trend for many areas such as banking and finance, retail, transporting goods, manufacturing, telecommunications, etc. With prioritised policies focusing on developing IT to a key sector, Vietnam is expected to be where Blockchain technology has many good conditions for development. This is also considered as an opportunity for start-up businesses and individuals to apply this new to be able to reach out to the region and the world.

by Editor | Aug 11, 2019 | News
President of the Republic of Finland Sauli Niinistö, who was honored with the World Leader for Peace and Cybersecurity Award presented by the Boston Global Forum on Global Cybersecurity Day December 12, 2018 at Loeb House, Harvard University, and Federal President of Germany Frank-Walter Steinmeier opened the 2019 Kultaranta Talks by discussing the change and future of Europe. In his opening remarks, President Niinistö challenged the audience to think what Europe has in common.
Organised for the seventh time now, the Kultaranta Talks have an interesting timing, said both Presidents in the opening discussion on 16 June. Finland has a new government, and Europeans have new representatives in Brussels. Moreover, Finland is getting ready for the EU Presidency. “This is a good moment to reflect on Europe’s challenges and the major tasks facing our continent and our Union,” President Steinmeier said.
The Presidents agreed that the EU will have many challenges to rise to. “The world’s political and economic centre of gravity is moving away from Europe. Europe has to reassess some of its own fundamental assumptions and to rethink its relations with the world’s major powers,” President Steinmeier said.
“The vision for the future is not very clear. It would be a surprise if we didn’t get any surprises in near future. Those are very difficult to predict, and that’s a demanding task for the European Union. The most central question is, whether we still have something in common. We should remind ourselves why we are together,” President Niinistö said.
Facing financial influence
In his speech, President Steinmeier mentioned superpowers and China, saying that while China is becoming closer to Europe, it is getting politically more distant. “How do we want this relationship to develop within the dynamics between the US, China, Russia, and Europe? Are we able to maintain our cohesion as the European Union?”
President Niinistö continued the thought by also analysing the financial influence of China from the point of view of the rules-based international system. He said that countries can be seduced by economic elements to forget the rules-based order. “Maintaining the cohesion will not be an easy task for the EU.”
From disintegration to cohesion
In their discussion, the Presidents also mentioned Brexit and the dividing lines it has created in Europe. President Steinmeier believed that the Europeans would be ready to learn the lesson from the Brexit. “If not the Europeans, who else would fight for the European cohesion?”
President Niinistö said that he is happy to see that the discussion on security and defence issues in the EU has started. “What kind of a union is a union which is based on outside help?”
While the Presidents discussed the challenges of European cooperation at length, they both agreed that there is no reason to be overly pessimistic. “It is our duty as presidents to be optimistic,” President Steinmeier said. President Niinistö agreed: “More and more political leaders are going back to the roots and understand that we do have a lot in common. And what we have in common, is becoming increasingly more important. When we recognise the common nominators, it will be easier to settle arguments.”
The original article can be found here.

by Editor | Aug 11, 2019 | News
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will bring many wonders. It may also destabilize everything from nuclear détente to human friendships. We need to think much harder about how to adapt.
Humanity is at the edge of a revolution driven by artificial intelligence. It has the potential to be one of the most significant and far-reaching revolutions in history, yet it has developed out of disparate efforts to solve specific practical problems rather than a comprehensive plan. Ironically, the ultimate effect of this case-by-case problem solving may be the transformation of human reasoning and decision making.
This revolution is unstoppable. Attempts to halt it would cede the future to that element of humanity more courageous in facing the implications of its own inventiveness. Instead, we should accept that AI is bound to become increasingly sophisticated and ubiquitous, and ask ourselves: How will its evolution affect human perception, cognition, and interaction? What will be its impact on our culture and, in the end, our history?
The full article can be found here.
To recognize the AI impact to humanity, the Michael Dukakis Institute for Leadership and Innovation (MDI) established the Artificial Intelligence World Society (AIWS) for the purpose of promoting ethical norms and practices in the development and use of AI. AI can be an important tool to serve and strengthen democracy, human rights, and the rule of law for solving important issues, such as SDGs.
by Editor | Aug 11, 2019 | News
A brief, non-invasive test using artificial intelligence (AI) has been found to identify patients with abnormal heart rhythm even when their rhythm seems normal.
The study, which involved almost 181,000 patients, is the first to use deep learning to find signals in heart scans that might be invisible to the human eye.
Writing in The Lancet, researchers from the Mayo Clinic describe how they trained an AI model to detect the signature of atrial fibrillation in 10-second electrocardiograms (ECGs), with 83% accuracy.
Atrial fibrillation is estimated to affect as many as six million people in the US alone, and is associated with increased risk of stroke, heart failure and mortality.
Further research is needed before clinical application is possible, but nevertheless the researchers speculate that it may one day be possible to use this technology as a point-of-care diagnostic test in a doctor’s surgery to screen high-risk groups. It might be also possible that the algorithm could be used on low-cost, widely available technologies, including smartphones.
This innovative AI application in medical healthcare is supported by AI World Society (AIWS) and Michael Dukakis Institute for Leadership and Innovation (MDI), which always promote applying AI technology for helping people achieve well-being and happiness.
The full article can be found here.

by Editor | Aug 11, 2019 | News
None of the big three internet foghorns—Facebook, Google, or Twitter—seems to have a clear plan for dealing with AI-generated fake videos, or “deepfakes,” ahead of next year’s presidential election, according to the chairman of the House Intelligence Committee.
Status update: Adam Schiff, a Democrat from California, said Friday that the three companies “have begun thinking seriously about the challenges posed by machine-manipulated media, or deepfakes, but that there is much more work to be done if they are to be prepared for the disruptive effect of this technology in the next election.”
Don’t panic: No need to freak out. There are, in fact, some emerging techniques for spotting videos that have been fabricated using AI.
Face-off: Deepfake videos use recent advances in machine learning to automatically swap faces in a video or perform other reality-blurring tricks. Simple deepfake tools can be downloaded from the web, and you can find many surreal examples of the results across the internet.
The worry: Image manipulation has been around for a long time, but AI is making sophisticated fakery more accessible. During an election, a deepfake could perhaps be used to be used to influence voters at the last moment. In May, a video of Nancy Pelosi that had been doctored to make it appear as if she were slurring her speech circulated rapidly on social media.
Cat and mouse: At the moment, there are a few ways to spot deepfakes. Irregular blinking is one telltale sign a video has been messed with, for example. But detection is something of an arms race, because an AI algorithm can usually be trained to address a given flaw.
Gotcha: This June, a new paper from several digital forensics experts outlined a more foolproof approach. It relies on training a detection algorithm to recognize the face and head movements of a particular person, thereby showing when that person’s face has been pasted onto the head and body of someone else. The approach only works when the system has been trained to recognize someone, but it could at least keep presidential candidates safe from attack.
Keeping quiet? Google actually provided some funding for this new research. So maybe these companies are keeping their cards close to their chest when it comes to deepfake detection. If you want to stay one step ahead of the fakers, that would certainly be a smart move.
The full article can be found here.
Boston Global Forum has organized conferences to discuss solutions by applying AI to solve cybersecurity issues. AI World Society’s the Social Contract 2020 includes cybersafety for citizens.








